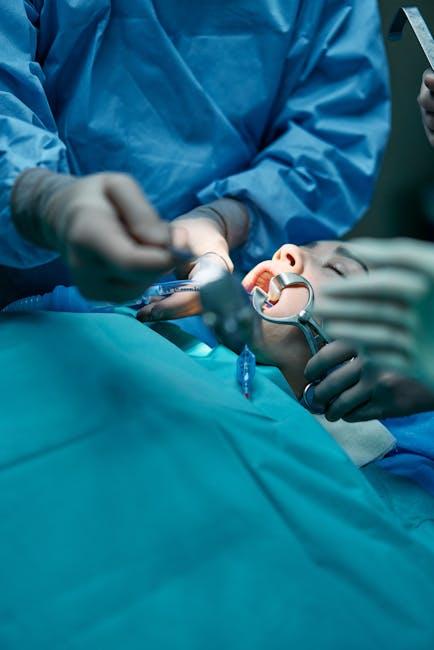
Mistakes in Dental Anesthesia Administration That Can Lead to Coma Identified
Contribution – Baku.ws
Introduction
Dental anesthesia is a cornerstone of modern dental care, enabling pain-free procedures ranging from routine cleanings to complex oral surgeries. However, like all medical interventions, anesthesia administration carries inherent risks. Among the most catastrophic and rare consequences are cases where improper administration leads to coma — a severe condition requiring immediate critical care. In this article, we dive into the common mistakes in dental anesthesia administration that can lead to such life-threatening scenarios. By understanding these pitfalls, dental professionals and patients alike can advocate for heightened safety measures, thus preventing avoidable tragedies.
The Importance of Safe Dental Anesthesia
Anesthesia ensures patient comfort but must be delivered with precision. Both local anesthesia (like lidocaine injections) and general sedation require detailed assessments, dosage calculations, and monitoring. Mistakes in any of these areas can cause serious complications including respiratory depression, oxygen deprivation, or toxic reactions — all potential precursors to coma.
Common Mistakes in Dental Anesthesia Administration
Understanding mistakes that lead to coma helps in mitigating these risks proactively. The following are the most critical errors:
- Incorrect Dosage Calculation: Overdosage of anesthetics like lidocaine can cause systemic toxicity, leading to central nervous system depression and coma.
- Failure to Assess Patient History: Neglecting to review allergies, medical conditions (e.g., liver or renal diseases), or previous anesthesia complications increases risk.
- Poor Airway Management: Inadequate monitoring of the patient’s airway under sedation can result in hypoxia, a leading cause of brain injury and coma.
- Ignoring Drug Interactions: Some medications interact with anesthetics potentiating their effects or causing unexpected toxicity.
- Lack of Continuous Monitoring: Insufficient monitoring of vital signs during procedure delays detection of adverse reactions.
- Improper Injection Techniques: Intra-arterial injections instead of targeted local injection can accelerate systemic absorption and toxicity.
- Inexperienced Personnel Administering Anesthesia: Lack of proper training or failure to follow protocols significantly raises the risk of critical errors.
How These Mistakes Can Lead to Coma
Here’s a simplified pathway explaining how anesthesia mistakes escalate into coma:
| Step | Error or Consequence | Impact on Patient |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Overdose or unintended systemic absorption | Central nervous system toxicity |
| 2 | Respiratory depression or airway obstruction | Insufficient oxygen delivery (hypoxia) |
| 3 | Failure to recognize early distress signs | Delayed intervention |
| 4 | Brain cell damage due to oxygen deprivation | Loss of consciousness progressing to coma |
Case Studies Highlighting Critical Mistakes
Several documented cases illustrate how anesthesia mishaps led to coma, reinforcing the need for vigilance:
- Case 1: A patient with undiagnosed liver impairment received a standard dose of lidocaine leading to accumulation and toxicity, resulting in seizures and coma.
- Case 2: Improper monitoring during sedation caused unnoticed airway obstruction, leading to prolonged hypoxia and subsequent coma.
- Case 3: An accidental intra-arterial injection caused rapid systemic absorption of anesthetic, leading to cardiovascular collapse and coma.
Best Practices to Prevent Anesthesia-Related Coma in Dentistry
Dental clinics and professionals should adopt stringent protocols to avoid anesthesia mistakes:
- Comprehensive Pre-Anesthesia Assessment: Detailed medical and medication history, allergy checks, and special risk evaluations (e.g., elderly, children, chronic illness).
- Individualized Dosage Calculation: Dosages adjusted to patient weight, health status, and procedure length.
- Experienced Staff Training: Regular training and certification in anesthesia administration and emergency response.
- Continuous Patient Monitoring: Use of pulse oximetry, blood pressure monitoring, and ECG during procedures under sedation or general anesthesia.
- Emergency Preparedness: Availability of resuscitation equipment and medications on-site.
- Clear Communication: Inform patients about risks, consent processes, and post-anesthesia care instructions.
Practical Tips for Patients Receiving Dental Anesthesia
Patients can play an active role in minimizing risks by following these tips:
- Provide full and honest medical history including any medications, allergies, or previous anesthesia problems.
- Ask your dentist about the type and amount of anesthesia planned and monitoring procedures.
- Follow all pre-procedure instructions, such as fasting or medication adjustments.
- Report any unusual symptoms immediately during or after the procedure.
- Arrange for someone to accompany you after sedation or general anesthesia.
Conclusion
Dental anesthesia is typically safe but mistakes in its administration can have devastating consequences including coma. Awareness of common errors and strict adherence to safety protocols are essential to protect patients. Both dental professionals and patients must cooperate to ensure thorough pre-assessment, skilled anesthesia delivery, and continuous monitoring throughout the procedure. Baku.ws remains committed to sharing critical health information and supporting safer dental care worldwide.